OSNR (Optical Signal to Noise Ratio) is a key measure of signal quality in long distance fiber optic communications. OSNR values are expressions of signal degradations caused by ASE (amplified spontaneous emission) noise added by optical components such as amplifiers along the transmission link.
Background
Typically, BER (Bit Error Rate) is an acceptable parameter to determine the quality of the transmission system along with Q-factor and optical eye-diagram analysis measurements. However, with CWDM and DWDM technology being used extensively for medium and long-haul communication systems, it becomes difficult to make Q-factor and optical eye-diagram analysis measurements. One will have to de-multiplex all the channels and perform these measurements on each individual channel. This can be time consuming, difficult, and expensive especially if you have many channels multiplexed together at the transmitter. In this scenario, optical spectrum analysis can be fast and useful to measure the performance of all the channels at once. This also allows to calculate the interference caused by the adjacent channels in these systems. Spectrum analysis also allows to calculate the ASE for each channel and can help system designers to design and scale their networks to meet any future demands.
What is OSNR?
OSNR is the ratio of the signal power to the noise power of an optical channel after passing through an optical network. It provides an estimate of how badly the noise power has affected the signal power. The higher the OSNR, the better it is for the overall system.
The general formula for calculating OSNR is:
OSNR=10*log(S/N)
where S is the signal power and N is the noise power, both expressed in watts or milliwatts.
OSNR values are most important at the receiver because a low OSNR value means that the signal will not be detected by the receiver. Typically, OSNR should be greater than 15 dB to 18 dB at the receiver, but this value will depend on many factors like the data rate, required BER etc. OSNR measurement methods are defined in IEC 61282-12 / b-IEC 61280-2-9 standards.
How is OSNR measured?
It can be measured using an Optical Spectrum Analyzer (OSA). There are many methods of measuring OSNR, depending on data rates and signal types. For 10G communications with ROADM present, in-band method is preferred.
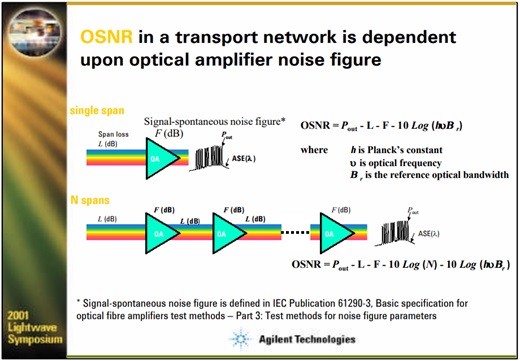
The image below describes OSNR calculations for single span and N-span networks.
Q-Factor and BER calculations
OSNR measurements can be used to calculate Q-factor and BER values using the following formula:
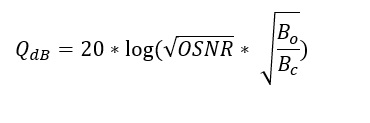
Where Bo is the optical bandwidth of the photodiode and Bc is the electrical bandwidth of the receiver filter.
Q-factor indicates the minimum signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) required to obtain a specific BER for a given signal. BER is defined as the ratio of number of bits in error to the total number of transmitted bits. A low BER value corresponds to high OSNR and Q-factor values.
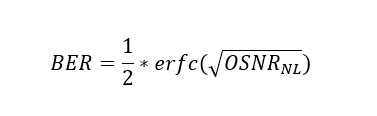
Summary
OSNR is a key parameter to evaluate the health of an optical network and to ensure excellent network performance and reliability. High OSNR values in a system can be achieved by using optics with high OSNRs. For questions on OSNR, BERs and optical transceiver networks, contact us.
Related Products



